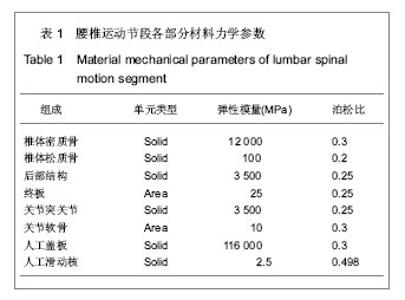
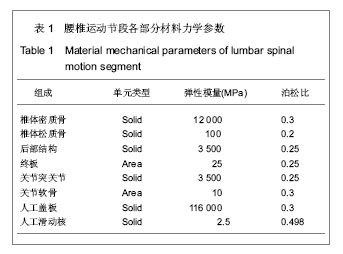
| [1] 吴刚,孙常太,黄公怡.人工腰椎间盘假体设计原理及现状[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(1):156-159.[2] Enker P, Steffee A, Mcmillin C,et al. Artificial disc replacement. Preliminary report with a 3-year minimum follow-up.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(8):1061-1070.[3] Hedman TP, Kostuik JP, Fernie GR,et al. Design of an intervertebral disc prosthesis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991; 16(6 Suppl):S256-260.[4] 苏秀云,刘蜀彬.Mimics软件临床应用[M].北京:人民军医出版社, 2011.[5] 成思源,谢韶旺.Geomagic Studio逆向工程技术及应用[M].北京:清华大学出版社, 2010:63-78.[6] 胡仁喜,刘昌丽. Pro/ENGINEER Wildfire 5.0工业设计实用详解[M].北京:电子工业出版社, 2010.[7] 邓凡平. ANSYS12.0有限元分析自学手册[M].北京:人民邮电出版社, 2009.[8] Lavaste F, Skalli W, Robin S,et al.Three-dimensional geometrical and mechanical modelling of the lumbar spine.J Biomech. 1992;25(10):1153-1164.[9] 钱忠来,唐天驷,杨惠林,等.腰椎椎间盘三维有限元分析[J].苏州大学学报:医学版,2002,22(1):4-7.[10] Yoganandan N, Kumaresan S, Voo L,et al. Finite element applications in human cervical spine modeling.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(15):1824-1834.[11] Panjabi MM.Cervical spine models for biomechanical research.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(24):2684-2700.[12] Kostuik JP. Intervertebral disc replacement. Experimental study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;(337):27-41.[13] Guyer RD, Ohnmeiss DD. Intervertebral disc prostheses.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(15 Suppl): S15-23.[14] 肖进,原林.人工椎间盘研制进展[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2001, 19(3):282-283.[15] Lemaire JP, Skalli W, Lavaste F,et al. Intervertebral disc prosthesis. Results and prospects for the year 2000.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;(337):64-76.[16] McAfee PC, Cunningham B, Holsapple G,et al. A prospective, randomized, multicenter Food and Drug Administration investigational device exemption study of lumbar total disc replacement with the CHARITE artificial disc versus lumbar fusion: part II: evaluation of radiographic outcomes and correlation of surgical technique accuracy with clinical outcomes.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(14):1576-1583.[17] Blumenthal S, McAfee PC, Guyer RD,et al. A prospective, randomized, multicenter Food and Drug Administration investigational device exemptions study of lumbar total disc replacement with the CHARITE artificial disc versus lumbar fusion: part I: evaluation of clinical outcomes.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(14):1565-1575.[18] Regan JJ, McAfee PC, Blumenthal SL,et al. Evaluation of surgical volume and the early experience with lumbar total disc replacement as part of the investigational device exemption study of the Charité Artificial Disc.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(19):2270-2276.[19] Siepe CJ, Mayer HM, Wiechert K,et al. Clinical results of total lumbar disc replacement with ProDisc II: three-year results for different indications.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(17): 1923-1932.[20] Zigler JE, Burd TA, Vialle EN,et al. Lumbar spine arthroplasty: early results using the ProDisc II: a prospective randomized trial of arthroplasty versus fusion. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2003; 16(4):352-361.[21] 李春海,叶伟,迟增德,等.不同位置植入SMH人工腰椎间盘对小关节应力分布的影响[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2007,25(4): 458-461.[22] 李康华,王华,雷光华,等.腰椎间盘切除与人工椎间盘对关节突关节内压力的影响[J].中国临床康复,2003,7(4):558-562.[23] Tropiano P, Huang RC, Girardi FP,et al. Lumbar total disc replacement. Seven to eleven-year follow-up.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(3):490-496.[24] 张宇坤,杨述华.人工腰椎间盘置换术的生物力学及中期临床疗效分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2007,27(5):374-377.[25] 黄东生,郝松林,刘尚礼,等.新型人工腰椎间盘的研制及其静态力学性能[J].中山医科大学学报,1998,19(2):124-127.[26] 徐义春,刘尚礼,张美超,等.人工腰椎间盘三维有限元模型的建立及其应力分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2003,23(3):173-176. [27] 王华,林博文,黎伟凡.人工腰椎间盘置换的有限元模型[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(13):2405-2408.[28] 万磊,李义凯. 有限元方法在腰椎研究中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2006,21(2):158-160.[29] 鲍春雨,刘晋浩. 基于CT图像人体脊柱腰椎节段逆向工程研究[J].机械设计,2008,25(9):16-18.[30] 张德胜,宋岳明. L3-L5三维非线性有限元模型的建立及临床意义[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2006,23(6):1250-1252.[31] Schmidt H, Heuer F, Wilke HJ. Dependency of disc degeneration on shear and tensile strains between annular fiber layers for complex loads. Med Eng Phys. 2009;31(6): 642-649.[32] Chen SH, Tai CL, Lin CY,et al. Biomechanical comparison of a new stand-alone anterior lumbar interbody fusion cage with established fixation techniques - a three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2008;9:88.[33] Nakamura T, Iribe T, Asou Y,et al. Effects of compressive loading on biomechanical properties of disc and peripheral tissue in a rat tail model.Eur Spine J. 2009;18(11):1595-1603.[34] Rohlmann A, Zander T, Rao M,et al. Applying a follower load delivers realistic results for simulating standing.J Biomech. 2009;42(10):1520-1526.[35] Meakin JR, Gregory JS, Smith FW,et al. Characterizing the shape of the lumbar spine using an active shape model: reliability and precision of the method.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(7):807-813. [36] 郝剑,朴哲,李继海,等.基于CT图像和逆向工程方法建立正常人体腰椎三维有限元模型[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(4): 593-596.[37] 李孝林.基于CT精细扫描构建人体胸腰段脊柱三维有限元模型的方法及意义[J].山东医药,2009,49(14):8-10.[38] 袁野,靳安民,何丽英,等.利用CT扫描及CAD技术建立腰椎活动节段的有限元模型[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2002,20(4): 298-300. [39] Büttner-Janz K, Schellnack K, Zippel H. Biomechanics of the SB Charité lumbar intervertebral disc endoprosthesis. Int Orthop. 1989;13(3):173-176.[40] 周宁琳.有机硅聚合物导论[M].北京:科学出版社, 2000:227.[41] 晨光化工研究院有机硅编写组.有机硅单体及聚合物[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 1986:295.[42] 谢遂志,刘登祥,周鸣峦. 橡胶工业手册(1)(修订版) [M].北京:化学工业出版社,2001.[43] 张承焱.硅橡胶在生物医学领域的应用[J].有机硅材料, 2002, 16(6):14-17.[44] 夏毅然,罗西友,赵成如,等.现代医用硅橡胶制品的性能及应用[J].有机硅材料,2002,16(3):22-23.[45] Chew SS, Marshall L, Kalish L,et al. Short-term and long-term results of combined sclerotherapy and rubber band ligation of hemorrhoids and mucosal prolapse. Dis Colon Rectum. 2003; 46(9):1232-1237. |